By Uttam Bane, Parag Madhukar Panse and Swapnil Dhanale
Below is an abridged version of the MVF Paper of the Year, “Value Enhancement of Differential Assembly”, by Uttam Bane, Parag Madhukar Panse and Swapnil Dhanale. You can read the complete version here. This paper won First Place at the INVEST Conference in November 2017, and thus it was the winner of the Bolton Scholarship Award.
Mahindra Tractor is market leader in India and to keep leadership we have to be Innovative and cost competitive. In Mahindra we are using VA/VE methodology as regular practice. The Team has taken the Tractor Differential System for our Value Analysis, which is shown in our CASE STUDY for Sustainable and Inclusive Growth – “Value Enhancement of Differential Assembly”. This will explain how we used VA/VE tools and kept the Basic FUNCTION the same, while resulting in a material cost reduction to the Company and no cost impact to the End Customer with the same Product FUNCTION Value.
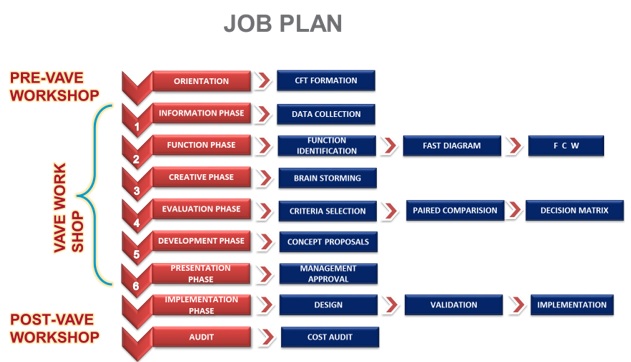
A. PRE-VA/VE WORKSHOP
1.Orientation Phase
The workshop was conducted for the team following the syllabus for the Value Analysis & Value Engineering methodology.

B. VA/VE WORKSHOP
2.Information Phase
The Team studied the component in detail and collected all the relevant information about the component (Differential sub assembly), including the raw material, the cost of front axle assembly, the general wall thickness, the weight of the component, and the number of idler bevel pinion gears.
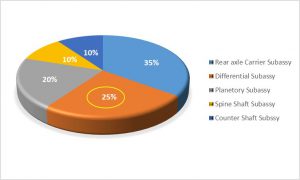
The graph shows the analysis of Differential Sub-assembly cost in the Transmission Rear Section Assembly. Rear Axle Carrier Assembly shows maximum cost contribution but a VA/VE study on that was done last year. The next largest contributor is the Differential Sub-Assembly with 25% of total cost of Transmission Rear Section Assembly. This was selected for a Case study.
3.Function Phase
a. Function Identification – Part Level
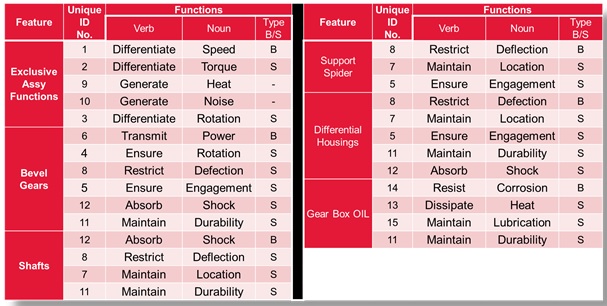
b. Function Identification – Assembly Level
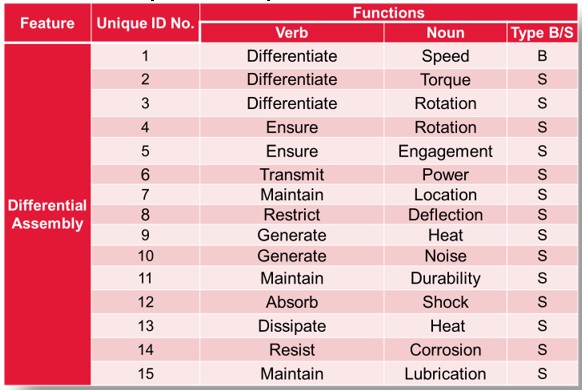
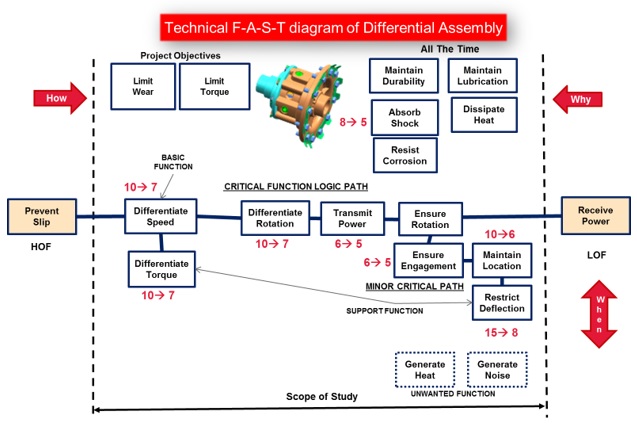
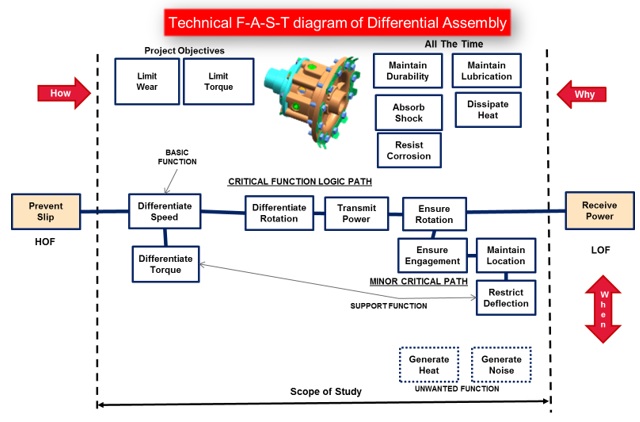
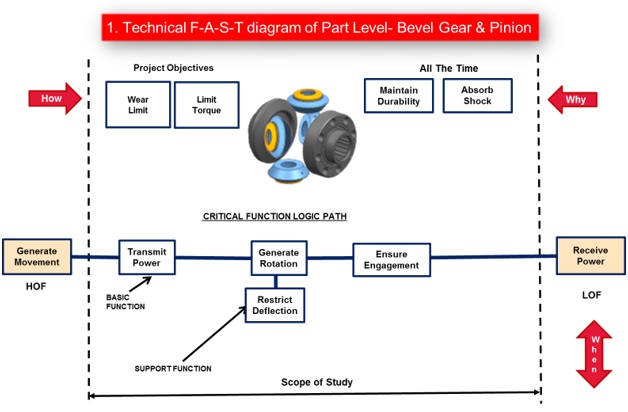
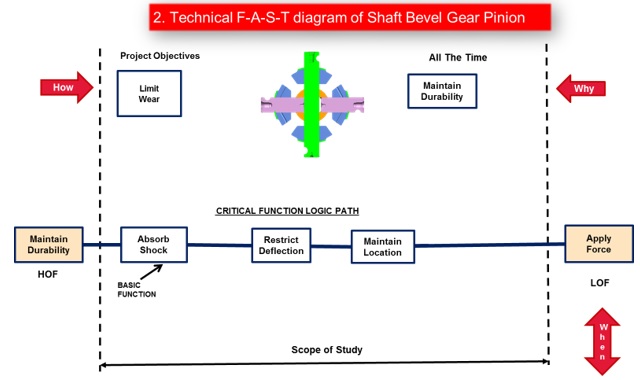
c. Technical F-A-S-T diagram
The existing Differential Sub Assembly as well as component level technical F-A-S-T Diagrams were prepared to have a better understanding of the component as well as assembly functions.
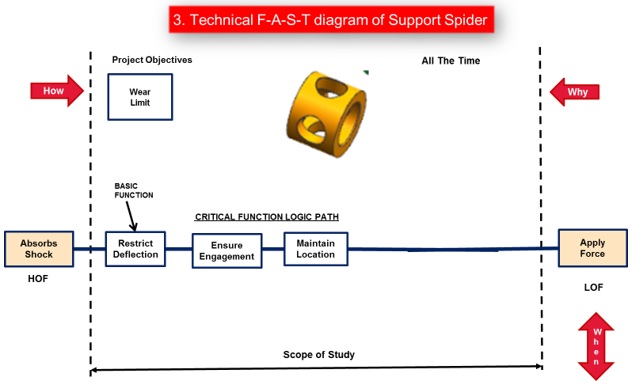
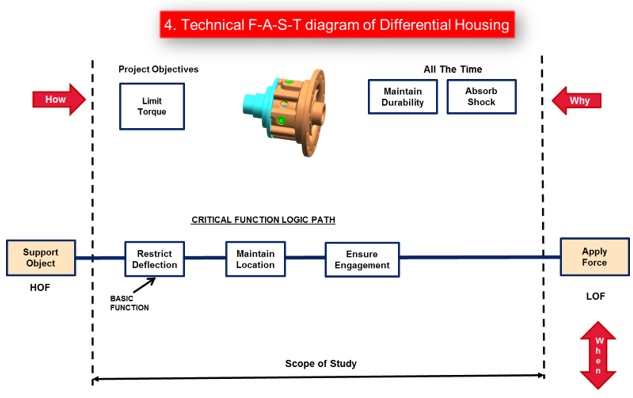
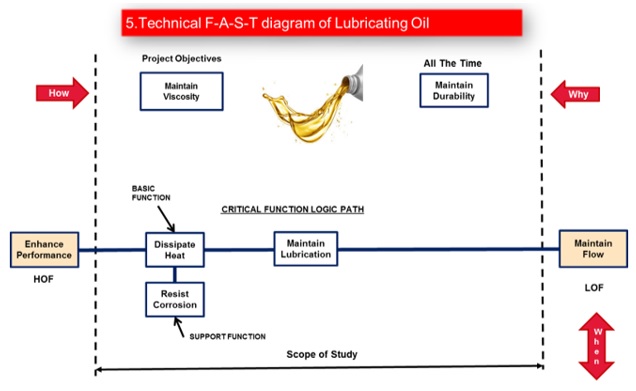
d. Function/Cost/Worth (F/C/W) Diagrams were prepared both at the Assembly Level and at the Part Level.
The Part Level F/C/W helped the team to determine the worth basis of individual component functions.
4.Creativity Phase
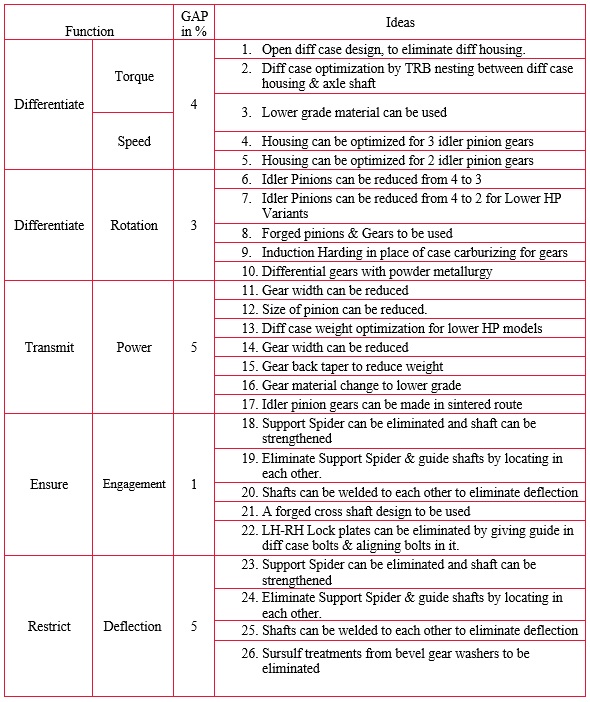
The team had a brainstorming session and generated 50 ideas with respect to gap observed functions. 37 Ideas were further segregated with respect to Gap observed functions during the F/C/W analysis.
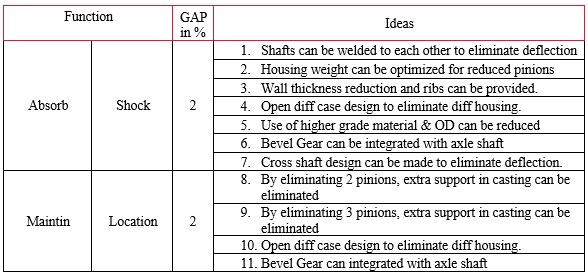
5.Evaluation Phase
The ideas were compared and evaluated using paired comparison and decision matrix technique.
a. Paired Comparison
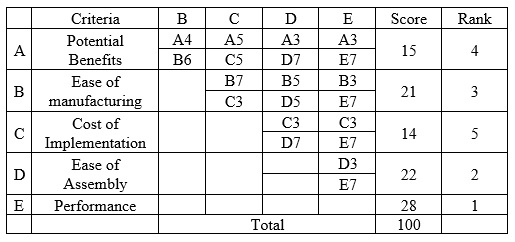
b. Decision Matrix
In the decision matrix, all 37 ideas further evaluated were separated with respect to gap function identified. Based on criteria, the highest-ranking ideas from each group were taken further for development. Other ideas were also feasible, but not cost effective, hence the Team decided to drop them. The highest ranked ideas from each Gap Functions were highlighted with color.
- Gap Function: Differentiate Torque / Speed
- Gap Function: Differentiate Rotation
- Gap Function: Ensure Engagement
- Gap Function: Maintain Location
- Gap Function: Restrict Deflection
- Gap Function: Absorb Shock
- Gap Function: Transmit Power
The following ideas have been selected from the gap identified functions from the F/C/W matrix:
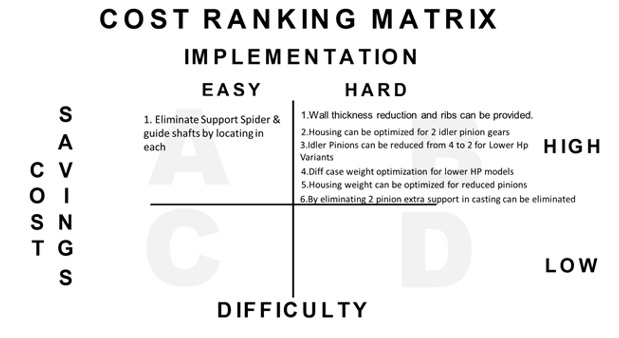
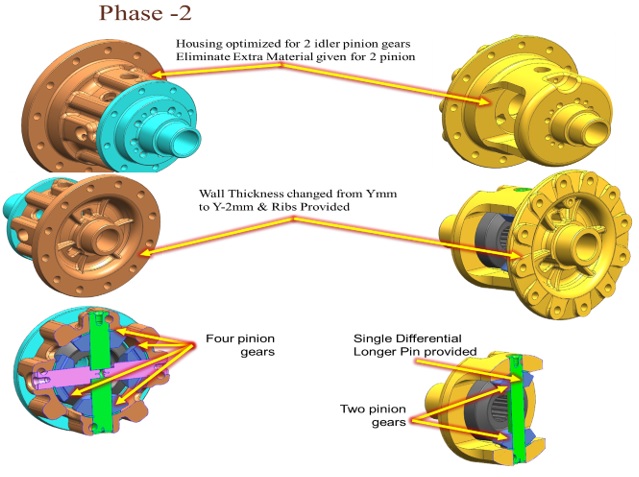
- Housing can be optimized for 2 idler pinion gears.
- Idler Pinions can be reduced from 4 to 2 for Lower HP Variants.
- Differential case weight optimization for lower HP models.
- Eliminate Support Spider & guide shafts by locating in each.
- Housing weight can be optimized for reduced pinions.
- Wall thickness reduction and ribs can be provided.
- By eliminating 2 pinions, extra support in casting can be eliminated.
c. Cost Ranking Matrix
These Ideas have been segregated in the Cost Ranking Matrix to prioritize them for implementation.
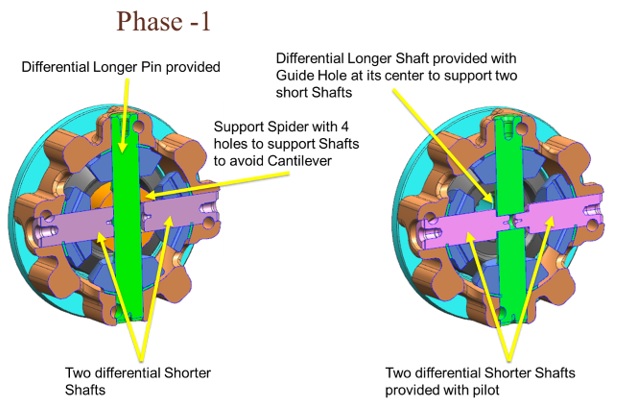
 6.Development Phase
6.Development Phase
Based on Cost Ranking Matrix, Ideas are divided into two proposals: one short term for quick implementation, and a second for the long term.
a. Short Term Proposal
b. Long Term Proposal
 7.Presentation Phase
7.Presentation Phase
The team had prepared the presentation document and send to VP Engineering & Project, Mahindra & Mahindra for approval.
C. POST VA/VE WORKSHOP
8.Implementation Phase
After receiving ‘Management Approval’, team has worked out detailed implementation planned and successfully implemented the Phase-1 proposal.
9.Audit Phase
This project reinforced that VA/VE has tremendous potential to save the cost without affecting the performance.
PROJECT RESULTS
The Team revised the FAST diagram to show that function is not eliminated, but the cost of the same functions are reduced by 25% with the Phase-1 & Phase 2 projects.